Tutorial Masked Output: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
This tutorial applies to all different OS and MXWendler versions. | |||
<div class="noprint"> | |||
== Introduction== | |||
</div> | |||
In this tutorial, an output mask will be created for a defined setup with a video projector. An image editing program (e.g. Photoshop / Gimp) must be used here. | In this tutorial, an output mask will be created for a defined setup with a video projector. An image editing program (e.g. Photoshop / Gimp) must be used here. | ||
<div class="noprint"> | |||
==Steps== | |||
</div> | |||
1. The selected video is loaded into the 'Preload' and active in the Layermanager. '''(A)''' <br> | 1. The selected video is loaded into the 'Preload' and active in the Layermanager. '''(A)''' <br> | ||
| Line 12: | Line 18: | ||
The graphic is stored as .png file on the desktop for the next step - processing into a mask in an image editor. '''(F)''' | The graphic is stored as .png file on the desktop for the next step - processing into a mask in an image editor. '''(F)''' | ||
''Tip: Masked outputs are an extremely effective tool for difficult projection projects. | ''Tip: Masked outputs are an extremely effective tool for difficult projection projects.<br>'' | ||
Of course, masks can also contain colour values and grey values. The mask is multiplied on the final output.'' | ''Of course, masks can also contain colour values and grey values. The mask is multiplied on the final output.'' | ||
[[File:Masked_Output_1.png|728px]] | [[File:Masked_Output_1.png|728px]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:35, 3 November 2020
This tutorial applies to all different OS and MXWendler versions.
In this tutorial, an output mask will be created for a defined setup with a video projector. An image editing program (e.g. Photoshop / Gimp) must be used here.
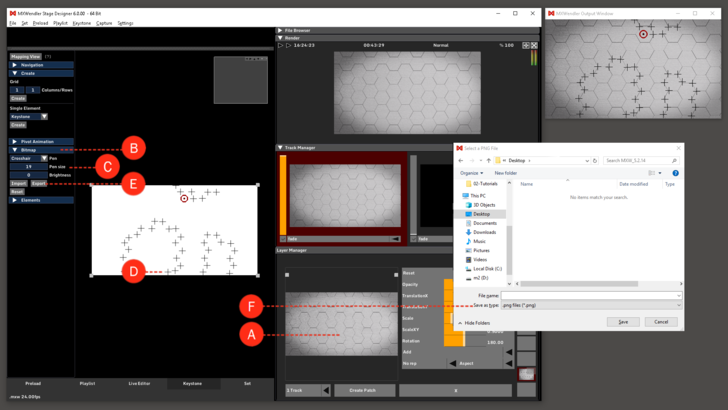
1. The selected video is loaded into the 'Preload' and active in the Layermanager. (A)
2. Go to the 'Bitmap' Submenu in the Keystone Tab. (B)
3. Select 'Crosshair' in the 'Brush' settings. The size of the Crosshair can be adjusted in the Brush Size settings. (C)
4. Specific selected points can be marked with Crosshair. (D)
With 'Export to Picture' the resulting graphic can be exported as an image. (E)
The graphic is stored as .png file on the desktop for the next step - processing into a mask in an image editor. (F)
Tip: Masked outputs are an extremely effective tool for difficult projection projects.
Of course, masks can also contain colour values and grey values. The mask is multiplied on the final output.
{{#mpdftags: pagebreak}}
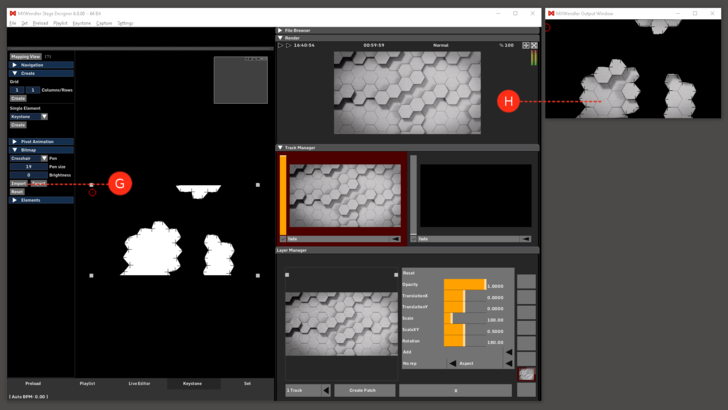
5. The finished mask is opened again after it is saved. Select 'Import from Picture' to load the mask. (G)
The mask is now active in the output window. (H)
Tip: PNG is used as a storage format as it contains alpha information and is lossless. The mask is exactly the same size as the display for the output window.